Variable Extrusion with Custom G Code

The project explores creating custom gcodes for 3d printers. It focuses on finding optimum extrusion and later on variating extrusion amounts for each distance within controlled parameters. Consumer available slicers (such as Prusa Slicer and Cura) do not give this kind of freedom to users. Therefore, I created a design workflow which allows for freedom in extrusion amounts.
Project was designed in Rhinoceros and Grasshopper, printed in Prusa i3 MK3S.
Design
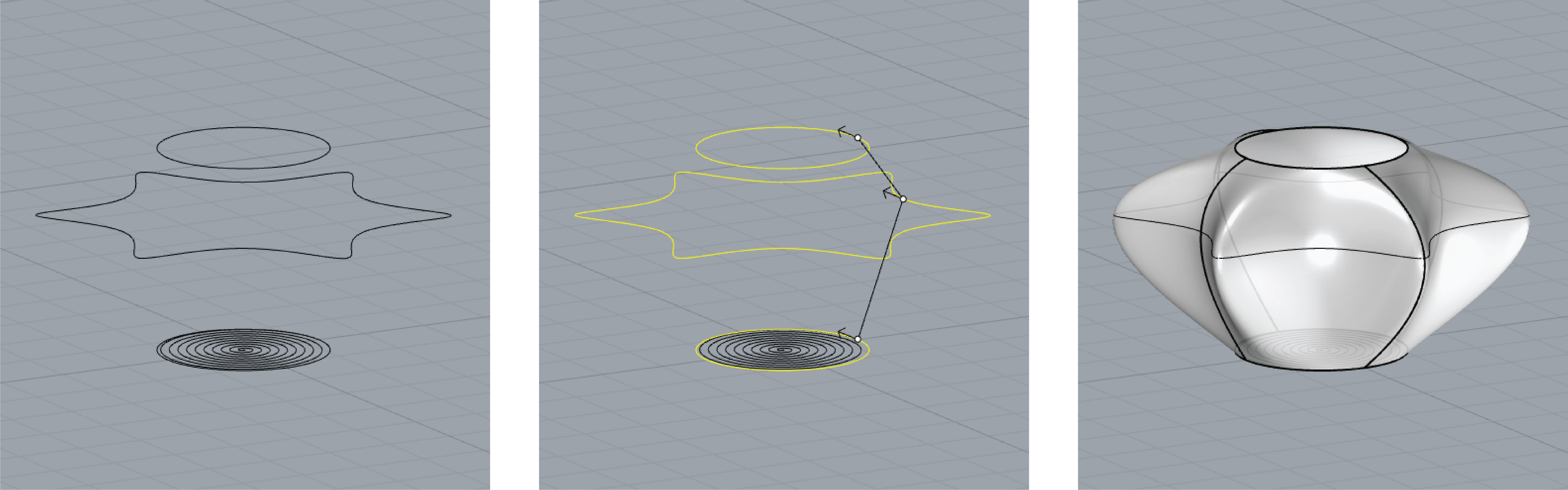
The beginning form is designed in Rhinoceros. It consists of 3 curves placed 20mm and 10mm away from each other vertically. Their centers are located at the same x,y coordinates. The curves, then, are lofted to create a surface. The base of the form is a spiral starting from the center of the bottom curve towards its perimeter. This form is actually only a vessel and can be replaced with forms of similar topology.
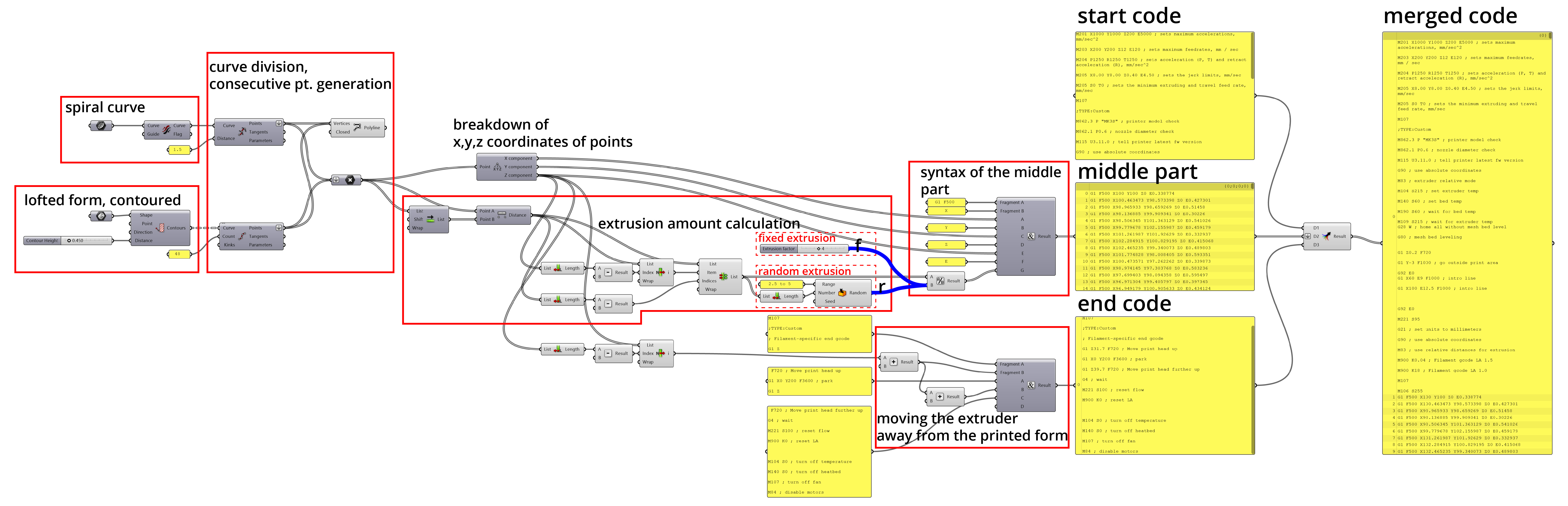
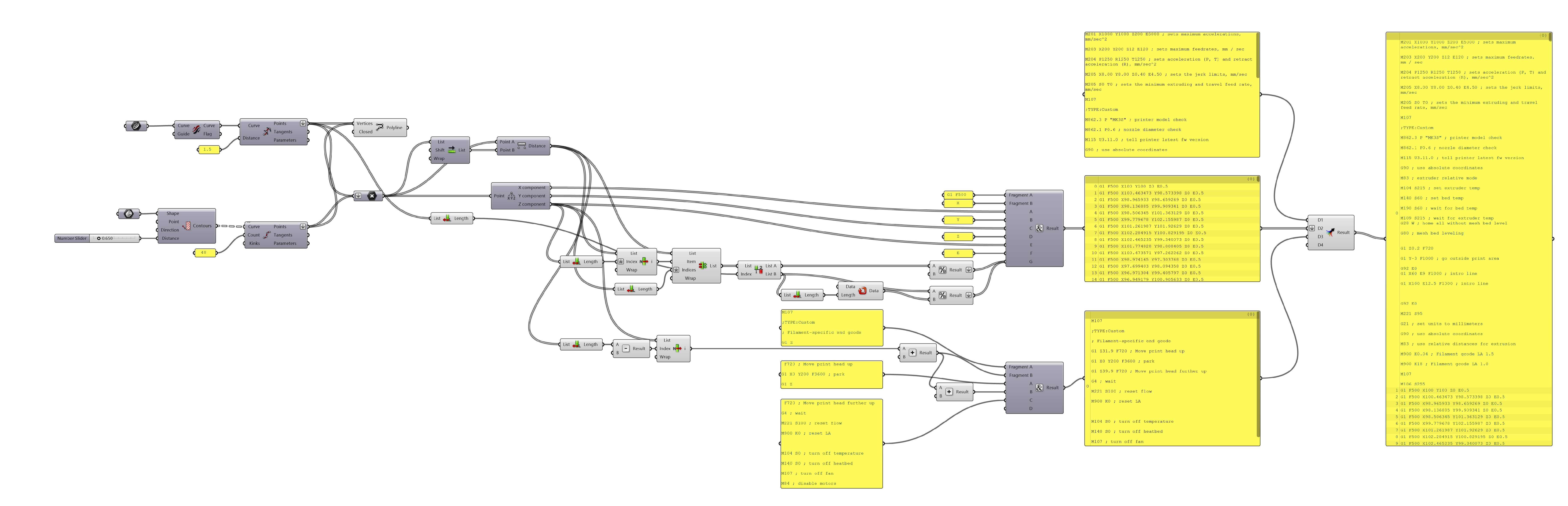
The algorithm to generate the gcode is created in Grasshopper.
About gcodes for 3d printers
Gcode is the most widely-used computer numerical control programming language for machines as well as 3d printers. Each line of code tells the printer to perform one specific action. Every line has a letter address. G codes direct the machine’s motion and function, while M codes direct the operations outside movements.
Gcodes for 3dprinters have 3 parts: the start code, the middle part and the end code. The start code prepares the machine for 3d printing: such as machine preparation, bed leveling, setting extruder and bed temperature. In the middle part, series of coordinates and extrusion amounts define the movement and printing of the forms. When the printing is finished, the end code prepares the machine to stop with commands for cooling, moving nozzle away from the print job, etc.
You can learn more about gcodes from Marlin’s website.
Since I used the Prusa i3 MK3S printer, I looked at a gcode file I created previously with Prusa Slicer to obtain and modify the start and end gcodes.
For the middle part of the gcode, I created an algorithm which imports spiral curve and lofted form from Rhinoceros. Lofted form is contoured to create a series of contour curves. All the curves are divided by a certain number to obtain points along them. The points are broken down to their x,y,z coordinates.
The x, y and z coordinates are directly fed to the middle part of the gcode as coordinates. The E variable in middle part, which is the extrusion amount, is found by a factor of the distance between two consecutive points. First I created a fixed extrusion component to find optimum extrusion. Later on, I wanted to give randomness to the extrusion amount within bounds which would print without problem. In the definition below, you can activate fixed extrusion by connecting f line and random extrusion by connecting r line to the division component (click on the image to see it bigger).
3d printing
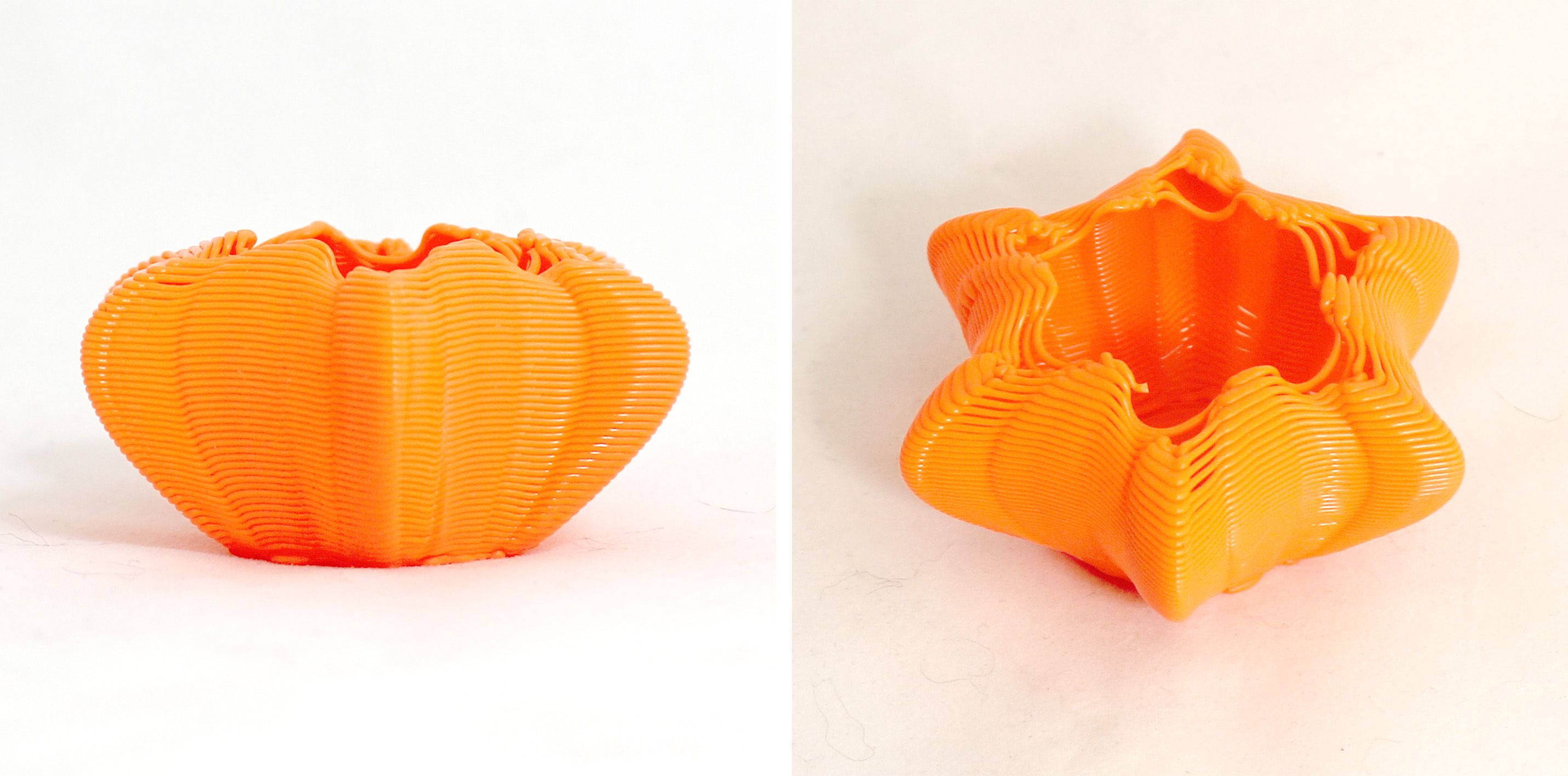
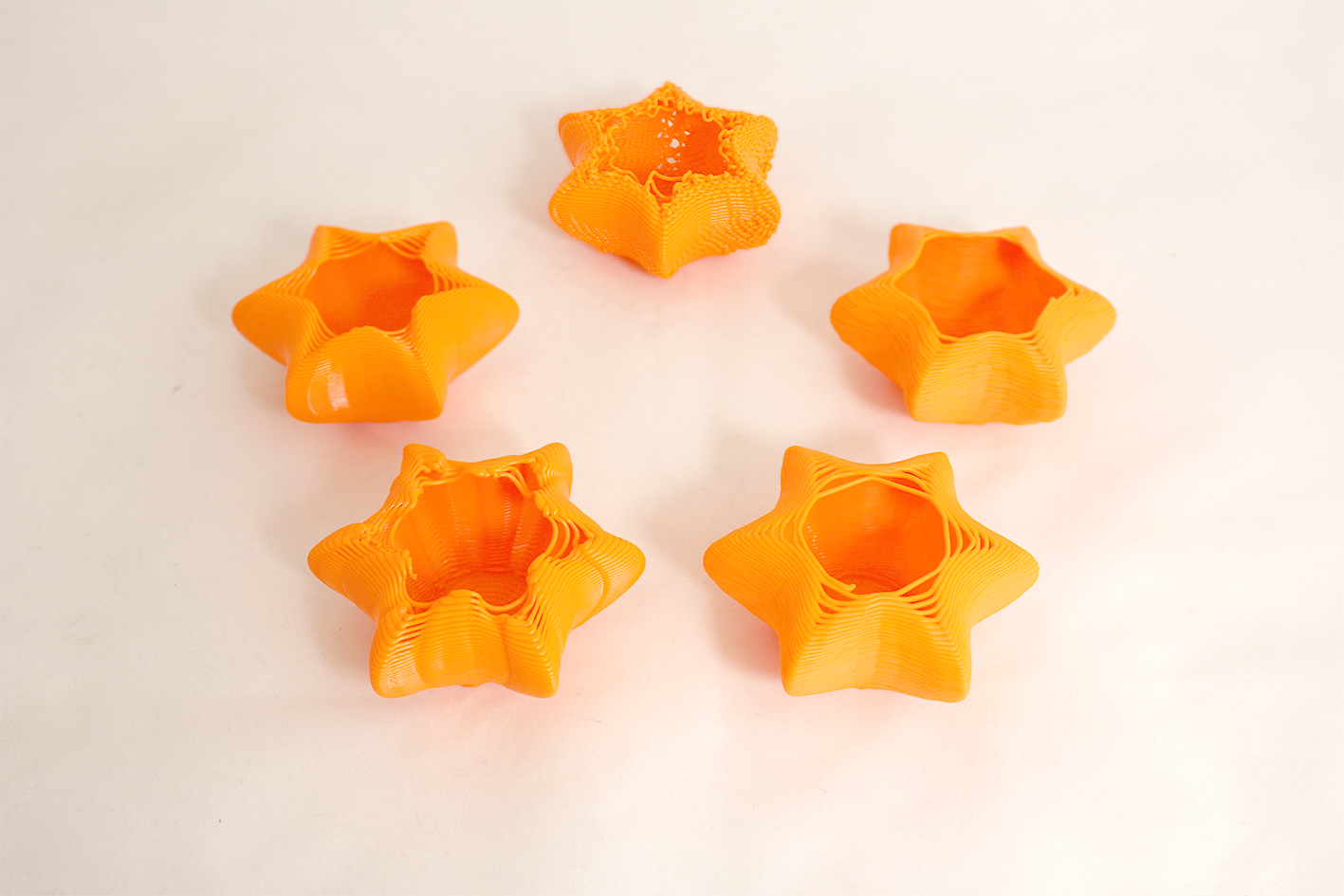
I started printing with fixed extrusion divider by 2 and contour height of 0.8mm. I observed that extrusion was too much and contouring distance was too much that the layers were not sticking to each other. The latter problem became more prominant in top layers.
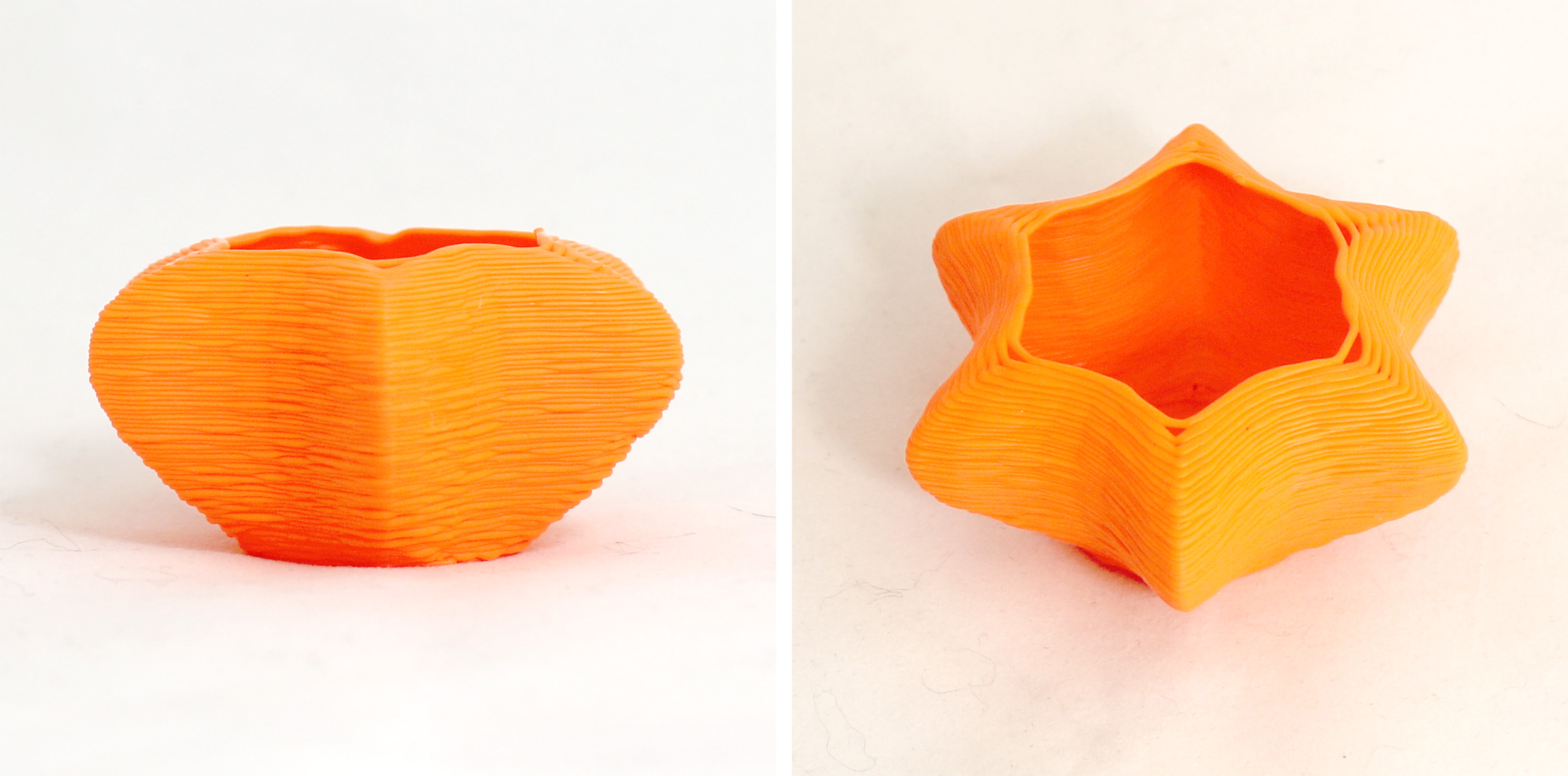
The second test uses a fixed extrusion divider of 4 and contour height of 0.45mm. This print came out nice, so these values can be used for a result similar to results from consumer available slicers.
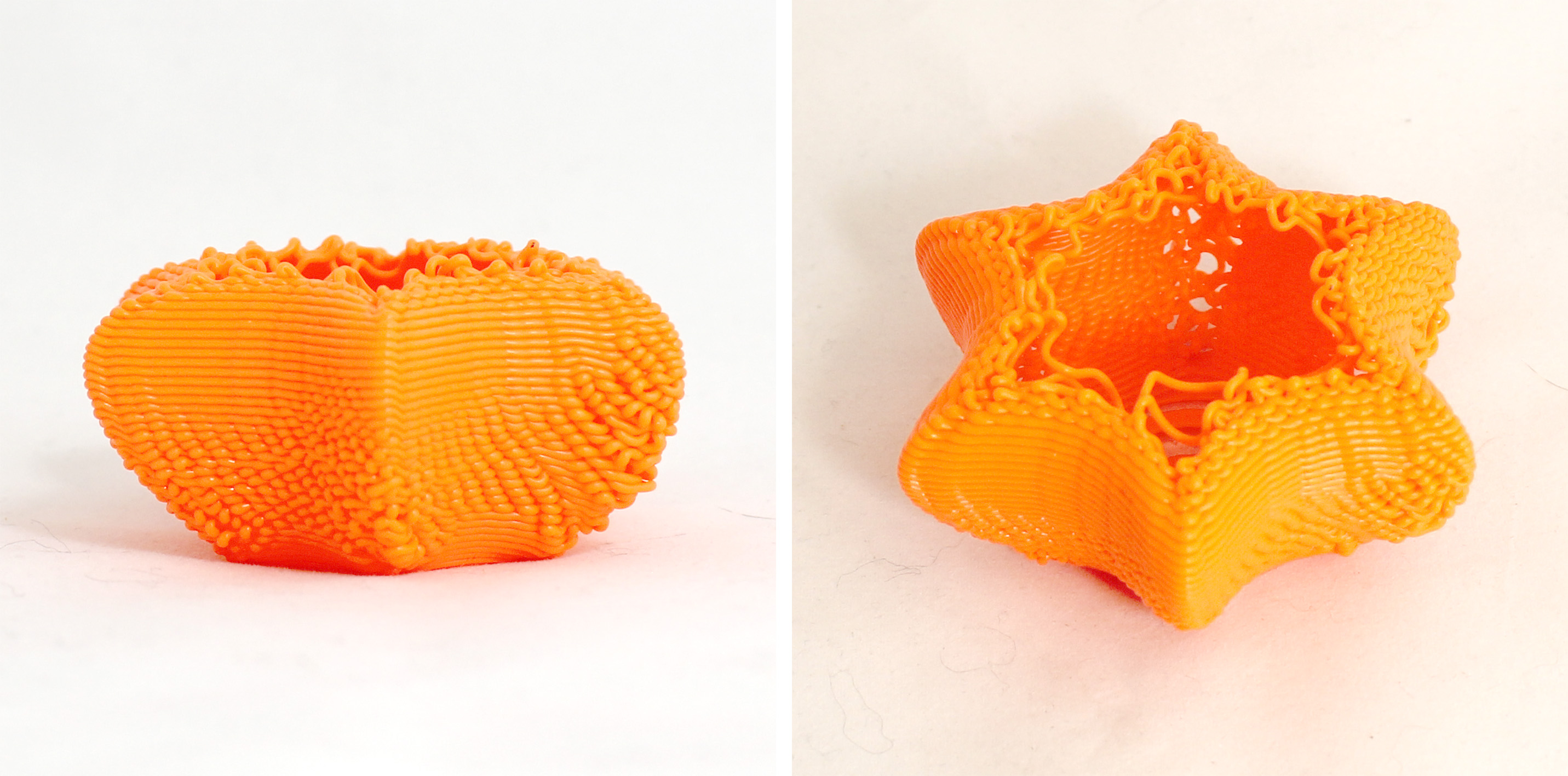
I started testing with random extrusion. From this point on, I did not change contour height but focused on extrusion amounts. The third test uses a random extrusion divider range between 2.5 and 5. I found this range too small that the end result was not very visible. The forth test uses a divider range between 1.8 and 6. The irregularity in extrusion was more prominent in the resulting form.
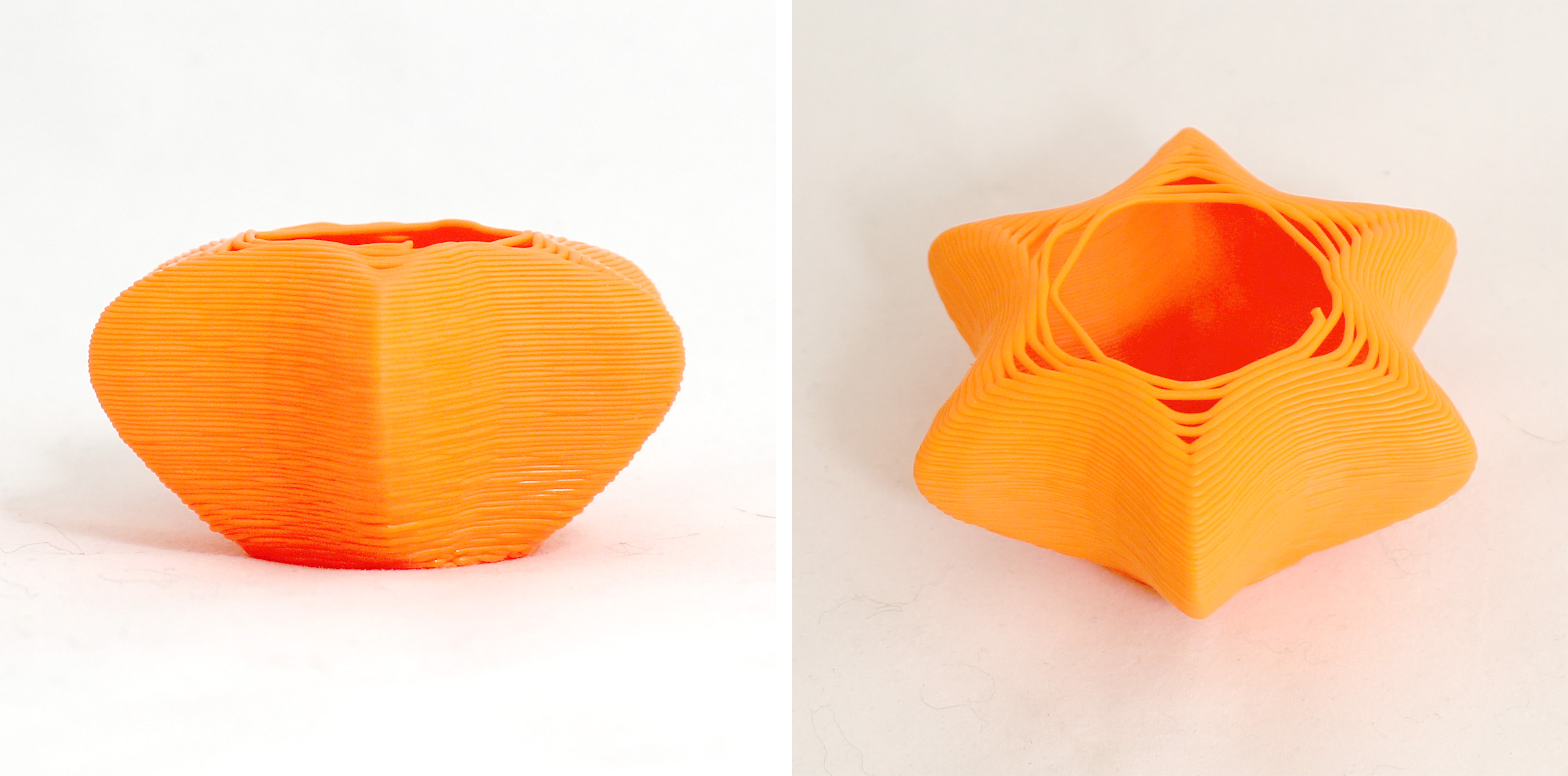
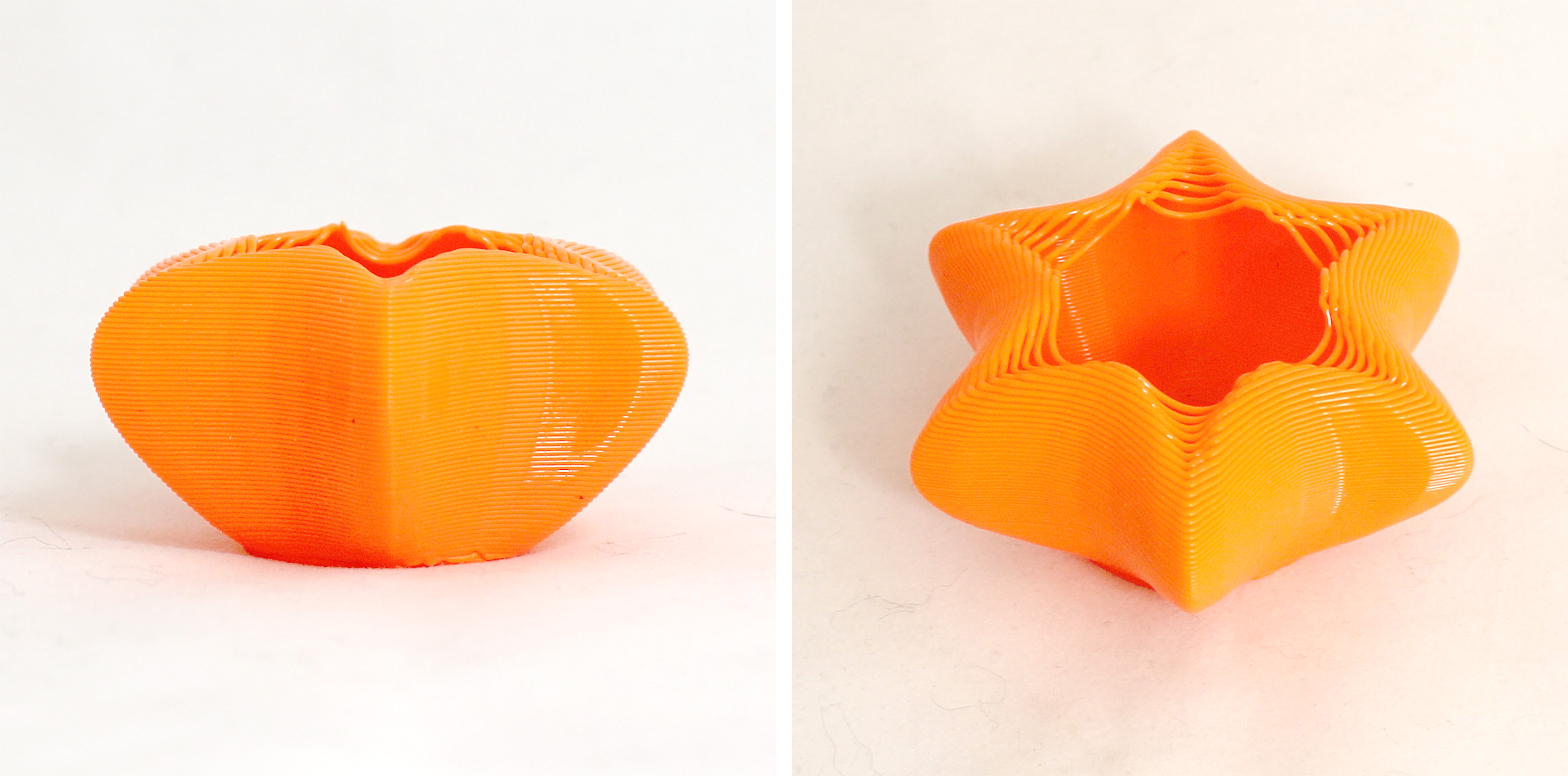
I moved on to exploring more procedural extrusions where I could vary but at the same time apply a pattern of extrusion dividers. For this form, I used 0.65mm contour height. The extrusion dividers pattern is 1.5, 7, 7 and 1,5. This pattern repeats until it reaches the end of the point list.